Software Methodologies
Two types: Plan-driven and Agile.
All processes involve:
- Software specification - What the software should do
- Design and implementation - How it should be organised and implemented
- Validation - Checking it does what the customer asked
- Evolution - Changing the software over time
Software specification
- Define which services are required and limitations of the system
- Idea: Create a document that anyone could use to build the system
Stages of requirements engineering:
- Feasibility study - Produce feasibility report
- Requirements, elicitation and analysis - Looking at existing documentation, talking to customers, discussion of features, etc.
- Requirements specification - Formal list of realistic requirements
- Requirements validation - Give the specification to the customer
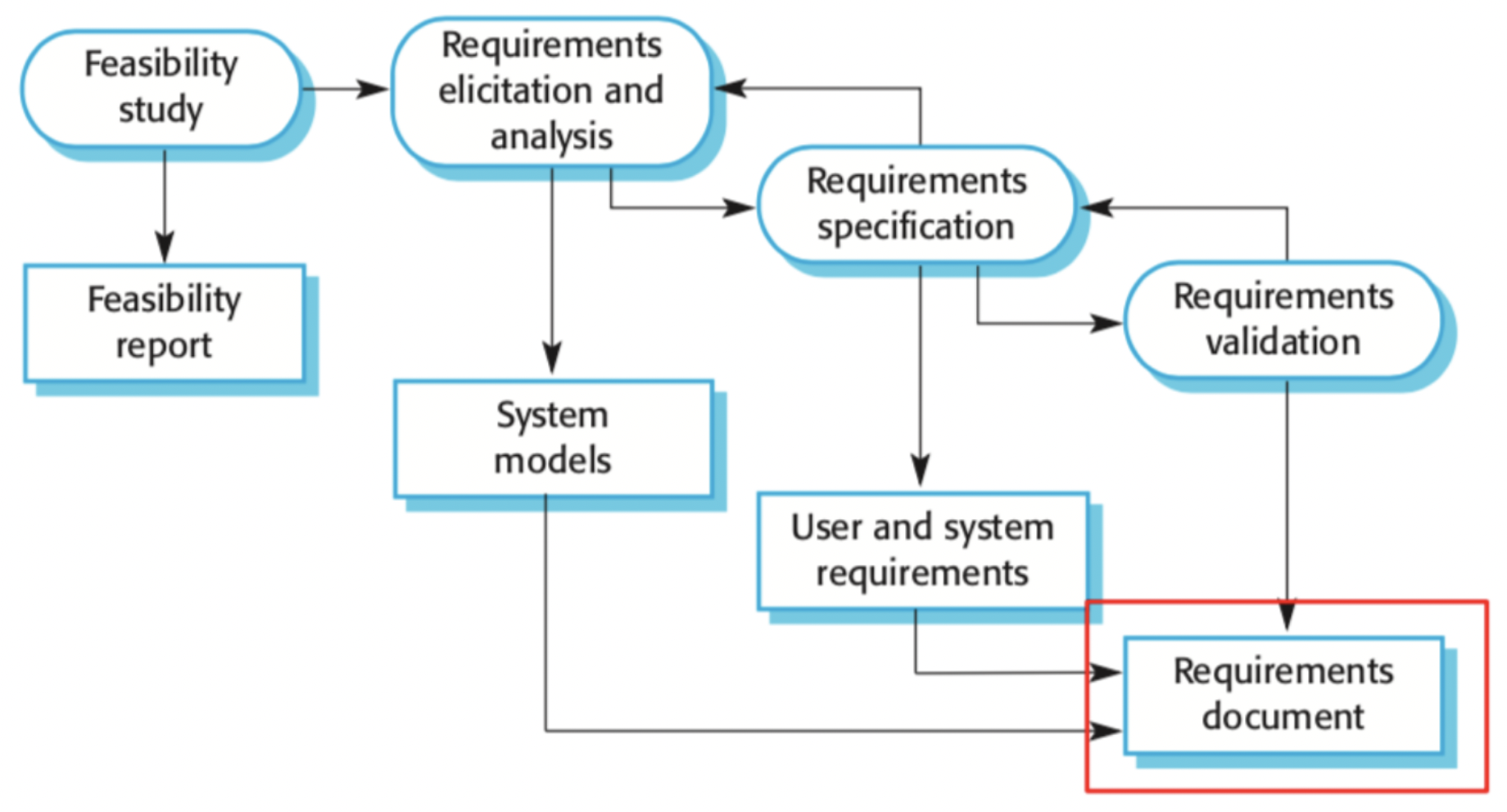
Requirements Engineering Stages
Plan driven methodologies
- All process activities planned in advance
- Progress measured against plan
- Do not deviate from plan
Waterfall Model
- Strict linear ordering of processes - one must be complete before the next begins
- Failure on any step means restarting
| Good for | Bad for |
|---|---|
| No changes in requirements expected | Changing requirements |
| Any sized team, any locations | Customer to see results quickly |
| Componentising sections of the system |
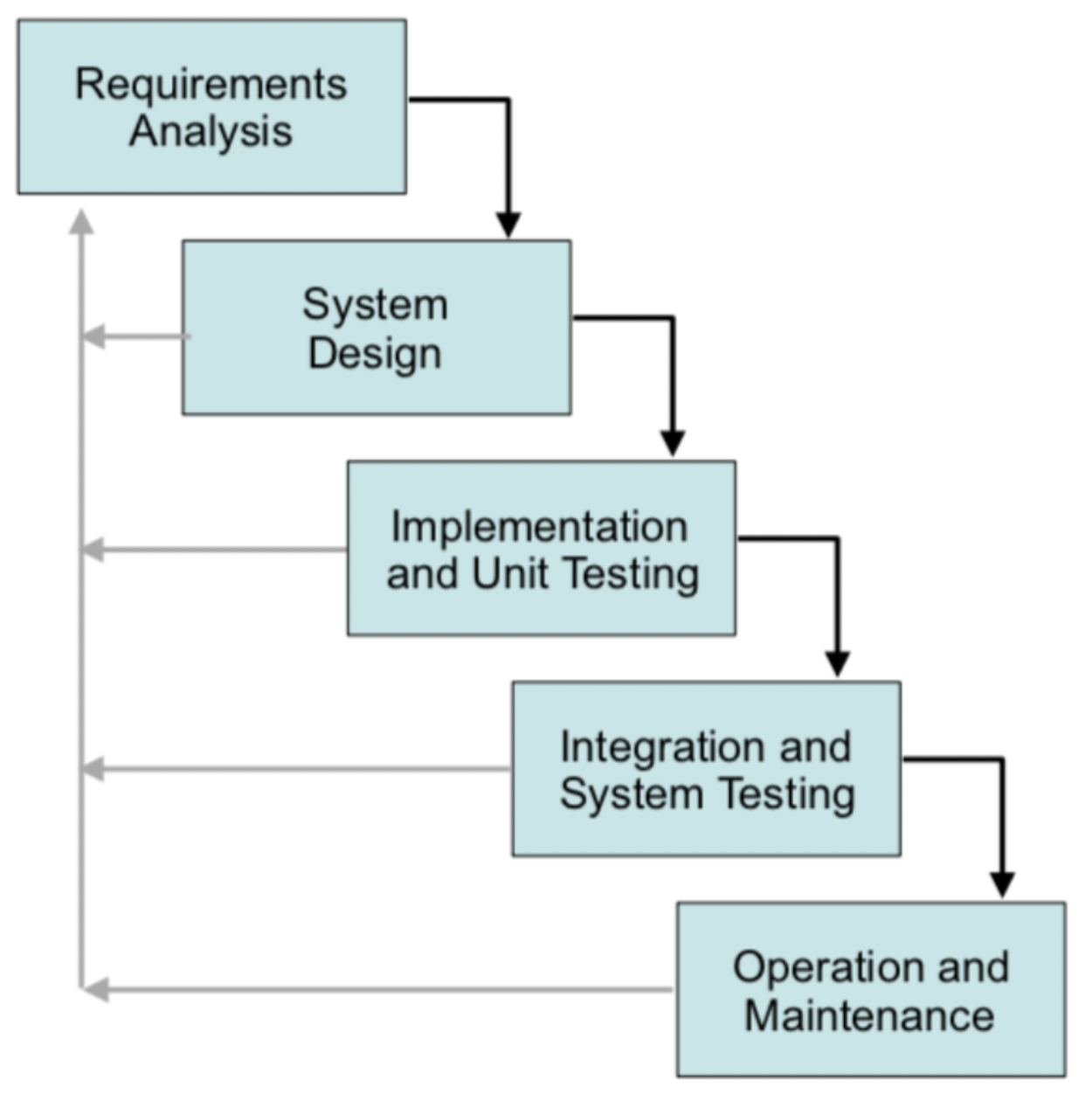
Waterfall Model
Incremental Development
- In stages, customer feedback between iterations
- Specification, development and validation can take place concurrently
- Each step is still planned in full, and tested against it’s specification
| Good for | Bad for |
|---|---|
| Reducing cost of changing requirements | Estimating development costs |
| Customer interacting with development cycle | Maintaining consistency with new features |
| Componentising sections of the system | Costs - expensive to redocument and redevelop |
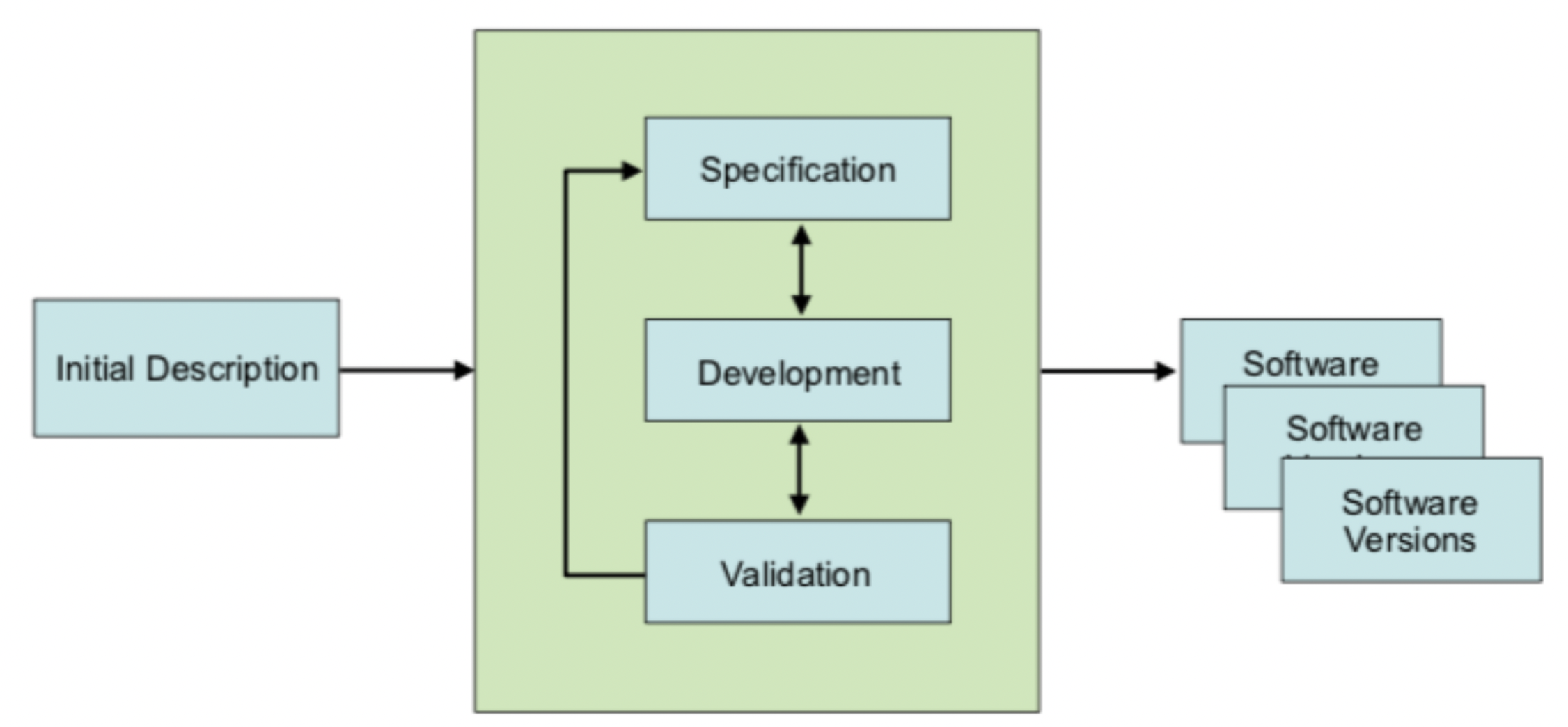
Incremental Development
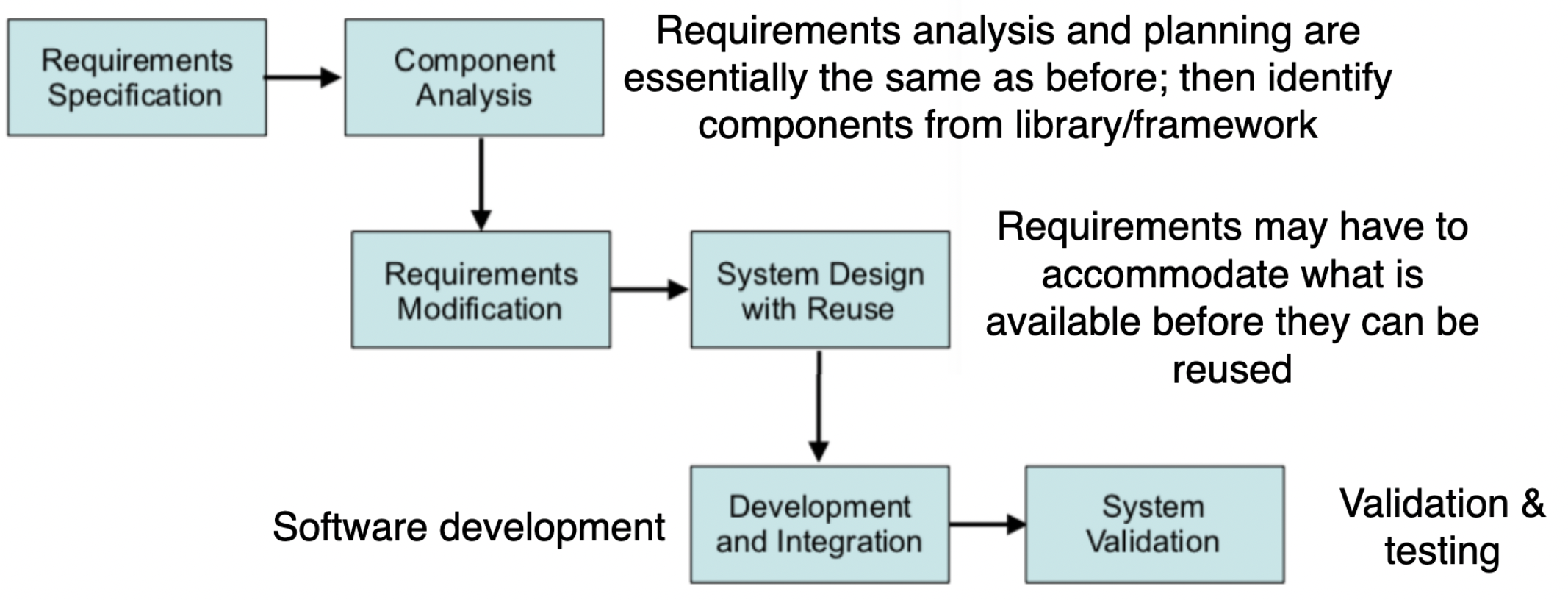
Reuse-oriented
- Uses common off-the-shelf systems (COTS), or large company libraries
- Typically good for webapps, frameworks etc.
- Development can be rapid and less costly
- Less testing needed on pre-implemented features
Reuse-oriented Software Engineering
Agile methodologies
- Specification, design and implementation interleaved
- Stakeholders give feedback at every stage
- Manifesto: Customer involvement, Incremental delivery, People not process, Embracing change, Maintain simplicity
- Less focus on documentation, needs heavy customer involvement and small, experienced teams
- Can produce prototypes & Minimum Viable Products
All agile methodologies share these disadvantages.
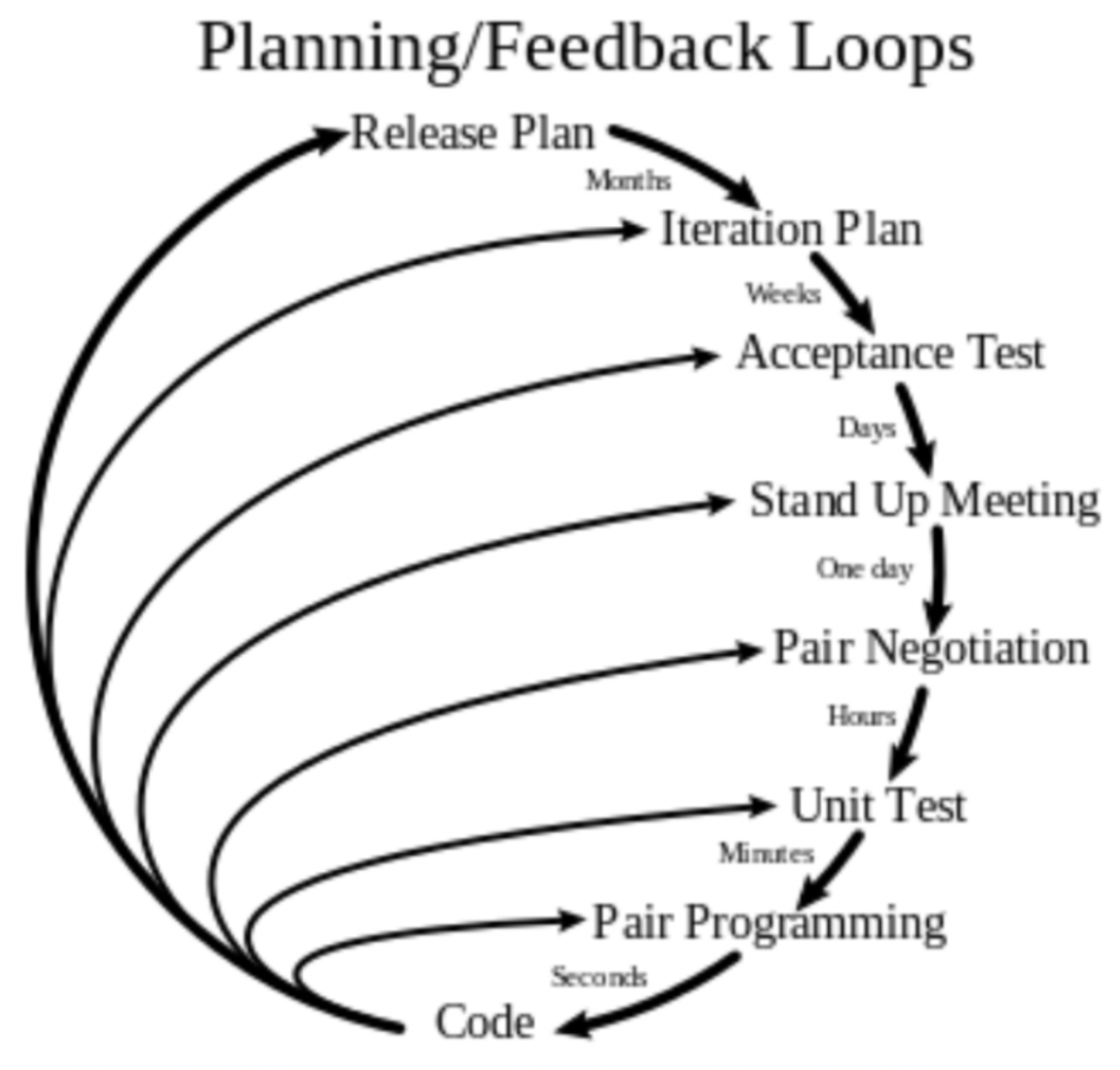
Extreme Programming (XP)
- Everything super fast: Incrementl delivery, fast iterations, automated builds and tests, continual code refactoring
- Customer builds every ~2 weeks
- Implement smallest possible change to create feature for atomic functionality
- Design for feature done just before implementing that feature
- Test-driven development: Write test before implementing
- Collective ownership: ≥2 people responsible for any section of code
Extreme Programming cycles
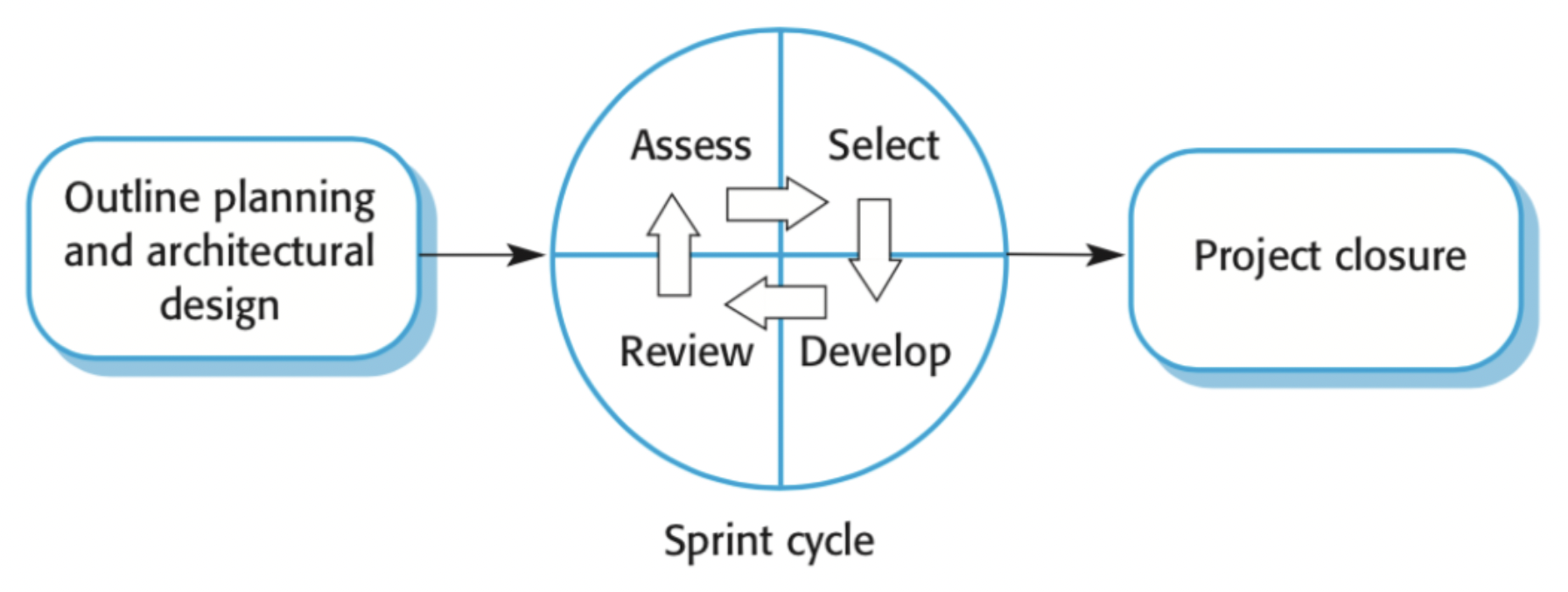
Scrum
- 3 stages: Outline planning, Sprint cycles, Project closure
- Sprints: ~2-4 weeks, daily meetings, items completed from backlog
- Scrum master: interfaces between dev team and customer
- Good if you want to manage a project in chunks, have unstable requirements and want smaller release cycles